Troubleshooting Workstations and Desktops#
This document provides guidelines for troubleshooting common issues with Vector desktops and workstations. By following this guide, you can often resolve problems without the need for a Repair Merchandise Authorization (RMA).
To mitigate unnecessary downtime with shipping and repair, Lambda may expect you to attempt basic troubleshooting before approving a request for RMA.
Note
When you encounter any issue with your product, your first step should be to file a support ticket. Doing so creates a record of your issue and allows our team to provide ongoing assistance if needed.
If possible, generate a Lambda bug report and attach the report to your ticket. This report provides our Support Team with valuable system information that can expedite the troubleshooting process.
Warning
Filing a support ticket is especially important if your warranty is nearing expiration. This ensures that potential issues are documented within the warranty period to safeguard your coverage for repairs or replacements.
Common issues#
The following tables identify issues that can be encountered with Vector systems and potential solutions. The first column gives a description of the issue. The second column provides troubleshooting approaches that can be taken to resolve the issue without the need for repair.
GPU#
Issue |
Possible solution(s) |
|---|---|
| No display on monitor |
|
| One or all GPUs missing | |
| Unable to access the BIOS when connected to a 4K monitor |
|
OS & software#
Issue |
Possible solution(s) |
|---|---|
| System doesn't boot to OS | Unable to access the BIOS:
|
| Missing drive(s) |
|
| Networking issue(s) |
|
| No mouse/keyboard input |
|
Power#
Issue |
Possible solution(s) |
|---|---|
| System doesn't power on | |
| Sudden power failure under load | |
Troubleshooting procedures#
This section provides step-by-step guidance for resolving specific issues outlined in the "Common issues" tables above.
Check power#
Note
Vector One: verify you're using the power button on the front of the device when attempting to start the system. You can read more about the buttons and ports on the Vector One in our getting started guide.
The power cord must be plugged directly into a wall outlet that can provide the appropriate voltage for your machine. Vectors use a large amount of power and can't reliably be used with uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs, or battery backups). The specific power requirements for your Power Supply Unit (PSU) can be found in our getting started guide.
Check that the power supply switch on the back of the machine is in the on position.
Power drain the machine:
- Unplug all power sources from your system.
- Press and hold the power button for 20 seconds.
- Plug the power cord back in and try to boot normally.
Reseat components#
System instability, intermittent hardware issues, and other hardware-related errors can often be resolved by reseating components.
For components not detected by the operating system, we recommend first trying to reseat the component to rule out partial connection, followed by trying the component in a different slot.
If after following the troubleshooting steps, you've determined that either the motherboard or component is faulty, contact support to request an RMA.
Before beginning, we recommend you use:
- An anti-static wrist strap.
- Motherboard manual included with your system to identify location of the components.
GPU#
See our video guides on how to re-seat GPUs on different Vector machines.
Reseating the graphics card can resolve display issues, system crashes, or recognition problems.
- Power off the machine and unplug all cables.
- Remove the GPU from the PCIe slot.
- Inspect the card and slot for any visible damage or obstruction.
- Firmly reinsert the GPU into the PCIe slot.
If a simple reseat doesn't resolve the issue, if applicable, try seating the component in a different available PCIe slot. If the GPU is detected by a different PCIe slot, this likely indicates a problem with the motherboard rather than the GPU.
Note
PCIe slots will vary depending on your system's motherboard model. If you're not sure which PCIe slots to use, contact support for assistance.
Memory#
Random Access Memory (RAM) module connection issues can cause system instability, random crashes, or boot failures.
Vector Pro: The GPU will need to be removed to access the memory modules.
- Power off the machine and unplug all cables.
- Unclip the affected RAM module from the slot.
- Inspect module contacts and slot for debris or damage.
- Securely reinsert the memory module into a different slot.
- Reboot the machine and verify the memory module is detected.
If a simple reseat doesn't resolve the issue, try seating the component in a different slot. For example, if DIMM_1 in slot_1 is not detected, move DIMM_1 to slot_2. If slot_2 detects the memory module, this indicates a problem with the motherboard slot_1.
Drives#
Trying alternative drive bays or slots can help diagnose connection or mounting-related performance issues.
- Power off the machine and unplug all cables.
- Remove the drive from its current SATA/M.2 slot.
- Inspect drive and slot for any signs of wear or damage.
- Move the boot drive to a different SATA/M.2 slot on the motherboard.
Verify BIOS settings#
Incorrect settings can lead to hardware recognition issues, boot problems, and reduced system reliability. Make sure your BIOS is configured with the following settings:
- Enter BIOS setup and navigate to the PCI Subsystem Settings. Verify that SR-IOV is set to Enabled.
- While in BIOS setup, also verify that the Fastboot option is Disabled.
- Save changes and exit BIOS.
Clear CMOS#
Clearing the CMOS resets your system's hardware configuration and returns all BIOS settings to factory defaults. This process can resolve hardware configuration conflicts that may not be apparent with standard troubleshooting.
- Unplug your machine from power.
- Locate the CMOS button on the motherboard. Refer to your motherboard manual for the exact location.
- Press and hold the CMOS button for 20 seconds to clear CMOS.
- Plug the machine back in and attempt to boot normally.
- After clearing CMOS, the BIOS will be reset to default configuration and you will need to reverify the BIOS settings (Fastboot Disabled, SR-IOV Enabled).
Update kernel parameters#
Kernel parameters allow you to modify system behavior and resolve hardware-specific issues at boot time. In some cases, adjusting these parameters can help address issues with PCIe devices and graphics hardware.
Add the pci=realloc=off parameter to your GRUB configuration:
- To do this, you'll need to edit the
/etc/default/grubfile. - Locate the line beginning with
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULTand addpci=realloc=offwithin the quotes after quiet splash. It should look like:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash pci=realloc=off" - Save the file and run
sudo update-grubto update GRUB with the new kernel parameter.
Boot into Live USB#
If you experience critical boot failures or your machine requires low-level system maintenance, a Live USB recovery environment provides a valuable diagnostics and repair tool. This method allows you to access and modify your system when standard boot methods fail.
- Create a bootable USB drive using our Lambda recovery image.
- Boot from the USB drive. When prompted, select the Try LambdaLabs Recovery without installing option to boot into the Live USB environment. This may take a few minutes.
- In the Live USB environment, verify that the networking/internet is working. You'll need to connect to your wifi manually if you're not on a wired connection.
- Open a terminal and run
lsblkto identify the boot drive, typically named/dev/nvme0n1. The partitions for the boot drive are typically named/dev/nvme0n1p1and/dev/nvme0n1p2. - Identify the boot partition by analyzing the partition size. The smaller of the two partitions will be the boot partition. In this example,
/dev/nvme0n1p1is the boot partition. - Mount the partitions to the
mntdirectory with the following two commands in sequence: sudo mount /dev/nvme0n1p2 /mntsudo mount /dev/nvme0n1p1 /mnt/boot/efi- With the partitions mounted, verify that
chrootis installed and working properly. Run the following command:wget files.lambdalabs.com/scripts/arch-chroot && chmod +x arch-chroot && sudo cp arch-chroot /bin - Next,
chrootinto themntdirectory to run the command:sudo arch-chroot /mnt - Perform a full update by running the command:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get full-upgrade - Run the command
exit, followed bysudo umount -R /mnt && sudo sync && sudo rebootto unmount the drive and reboot.
Check system motherboard model#
If you have a Vector desktop with a WRX80 motherboard and a 4K monitor, when the system boots, the monitor should display the ASUS logo screen; however, it does not show the prompts to access the BIOS. If you press F2 to access the BIOS, the monitor continues to not display the BIOS prompts until after the system restarts. The system boots normally if you don't interact with it, but the video only displays when the Ubuntu OS boots successfully.
You can determine whether your system has the WRX80 motherboard by running:
Your system has a WRX80 motherboard if the command returns: Product Name: Pro WS WRX80E-SAGE SE
The best solution at this time is to switch to a non-4K monitor, like 1080p.
No audio from aux ports on Vector One#
Known issue with Ubuntu 22.04#
A bug in Ubuntu 22.04 can cause the front aux port to not recognize audio devices on some Vector One desktops. This issue can be resolved by upgrading to Ubuntu 24.04.
Test the rear audio port#
If your machine does not recognize audio devices connected to the front aux port, try using the rear audio port, which is lime green in color.
Update packages and drivers#
Install the latest software packages and device drivers by running the following command in the terminal:
After the system restarts, test the aux ports again to see if the issue is resolved.
Reinstall audio packages#
If the issue persists after updating the drivers, try reinstalling the audio packages using the following commands:
sudo apt-get -y install --reinstall alsa-base alsa-topology-conf alsa-ucm-conf alsa-utils gstreamer1.0-alsa:amd64
sudo apt-get -y install --reinstall libasound2 libasound2-data libasound2-plugins
sudo apt-get -y install --reinstall gstreamer1.0-pulseaudio:amd64 libpulse-mainloop-glib0:amd64 libpulse0:amd64 libpulsedsp:amd64 pulseaudio pulseaudio-utils
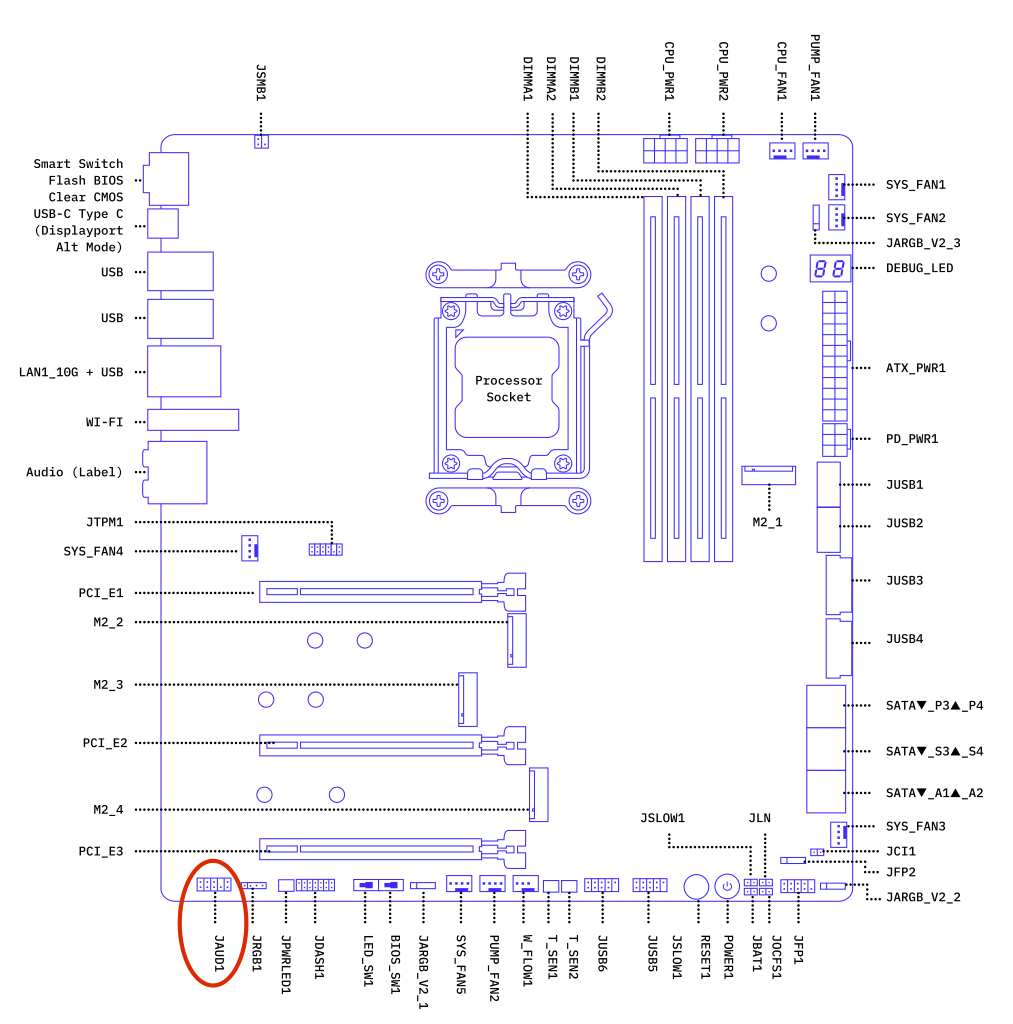
Check the motherboard HD audio cable connection#
Reseat the HD audio cable connected to the front audio port on the bottom-left of the motherboard and make sure the cable is securely connected.
Refer to the image below for the location of the HD audio cable port on your motherboard, labelled JAUD1:
Contact Lambda#
If you can’t discover the cause for the issue you are experiencing, contact Lambda Support and provide us with your Lambda bug report.